Key Insights
Differences Between HRM and SHRM
Unlike HRM, which deals with people and processes, SHRM refers to the strategic integration of HR functions with the business agenda. Recognising such differences enables an organisation to tackle immediate challenges whilst planning for greater expansion.
Human Resource Management Meaning
HRM refers to the management of the workforce and other employee-related functions. It covers day-to-day HR processes, such as recruitment, payroll, and statutory compliance.
Strategic Human Resource Management Meaning
SHRM concerns the integration of HR strategies with the corporate objectives on a long-term basis. It ensures that a business continually builds a competitive workforce that adapts to the future challenges.
Differences Between HRM and SHRM
In the context of modern business, understanding the distinction between HRM and SHRM is pivotal. As the name suggests, HRM focuses on managing the workforce and satisfying daily employee demands, whereas SHRM aligns human resources activities with strategic organisational objectives.
Understanding their distinction enables an organisation to create an efficient workforce that propels the organisation toward its strategic goals. Moreover, these distinctions offer HR practitioners insight into selecting the most suitable HR strategy in line with the organisation’s objectives. Such understanding provides organisations the ability to be flexible in the immediate future while ensuring viability in the future.
What is HRM (Human Resource Management)?
Human Resource Management (HRM) encapsulates all employee-related activities managed within an organisation. It takes charge of the recruiting, employee relations, payroll, performance management, and compliance functions to ensure the effortless functioning of the workforce.
Unlike SHRM, HRM’s primary focus is on the immediate and operational employee concerns, which is equally important as addressing long-term workforce planning. Furthermore, HRM assumes the responsibility of preserving order in the workplace and enhancing employee relations.
This approach ensures that HRM promotes equal opportunity and develops a seamless, regulated framework, thereby enhancing organisational performance and employee gratification.
Objectives of HRM
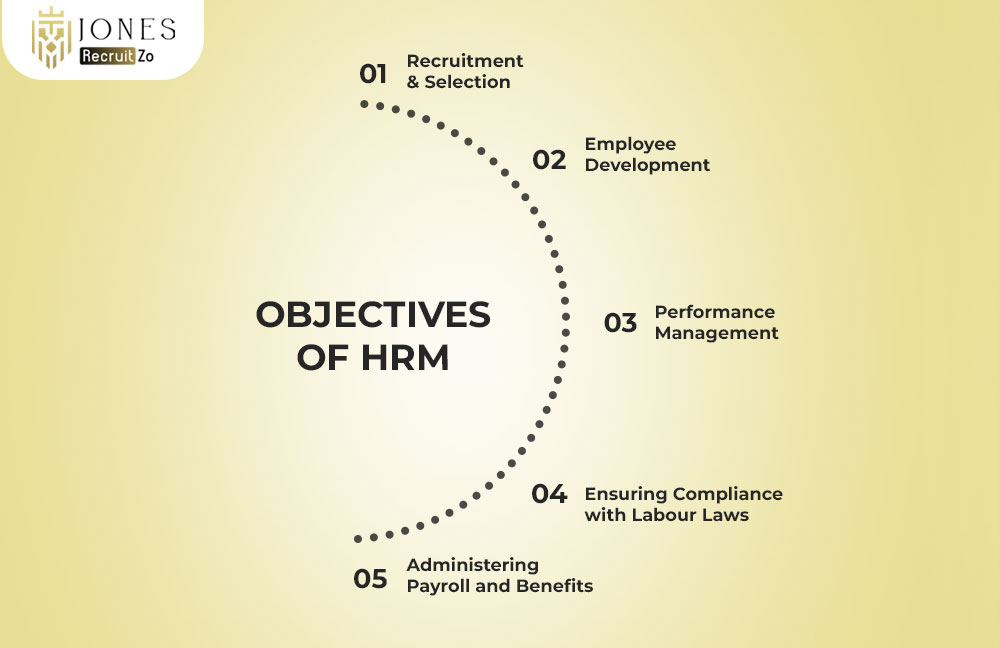
The objectives of HRM revolve around managing people effectively to ensure organisational stability. Below are the key areas where HRM plays a vital role,
Recruitment & Selection
Structured recruitment and selection processes are essential to bringing in the appropriate talent. This includes developing job descriptions, reviewing applications, and selecting candidates through a structured process. Recruitment and selection conducted through HRM strengthen the overall talent pool by upholding a fair and efficient process.
Employee Development
The employee development function of HRM centres on providing training and skill enhancement programmes. The goal is to provide employees with sufficient knowledge to execute their jobs well. This increases engagement, job satisfaction, and loyalty in the long run.
Performance Management
The HR department works to ensure each and every employee meets the expected standards of work and contributes to the greater corporate goals. The HR department provides each employee an appraisal system through which they get feedback and get put on performance improvement plans in a timely manner. This develops a culture of responsibility and motivates employees to better their performance.
Ensuring Compliance with Labour Laws
Every single aspect of an organisation’s operations must be scrutinised to ensure automation-compliance with the labour laws and any other regulations that govern the workplace. This checking includes wage laws, employee rights, safety regulations, and the relevant safety standards in the workplace. This compliant behaviour helps in reducing the risk of litigation and ensures the maintenance of a safe work environment.
Administering Payroll and Benefits
HRM handles compensation, benefits, and payroll management for employees. It ensures salaries are processed accurately and benefits such as insurance or leave entitlements are provided. This fosters trust and financial security among employees.
What is SHRM (Strategic Human Resource Management)?
SHRM elevates the role of human resource management from routine HR activities to matters directly connected with the company’s strategy. SHRM ensures that HR policies correspond to the company’s long-term objectives. It aims to build and nurture a workforce that enhances the company’s competitiveness, agility, and sustainability. It requires planning for and addressing skill gaps in a timely manner.
SHRM enables a company to embed flexibility within its workforce, thereby responding swiftly to shifts in the market. When the people strategy is combined with the business strategy, SHRM contributes towards driving innovation and sustainable growth.
Objectives of SHRM
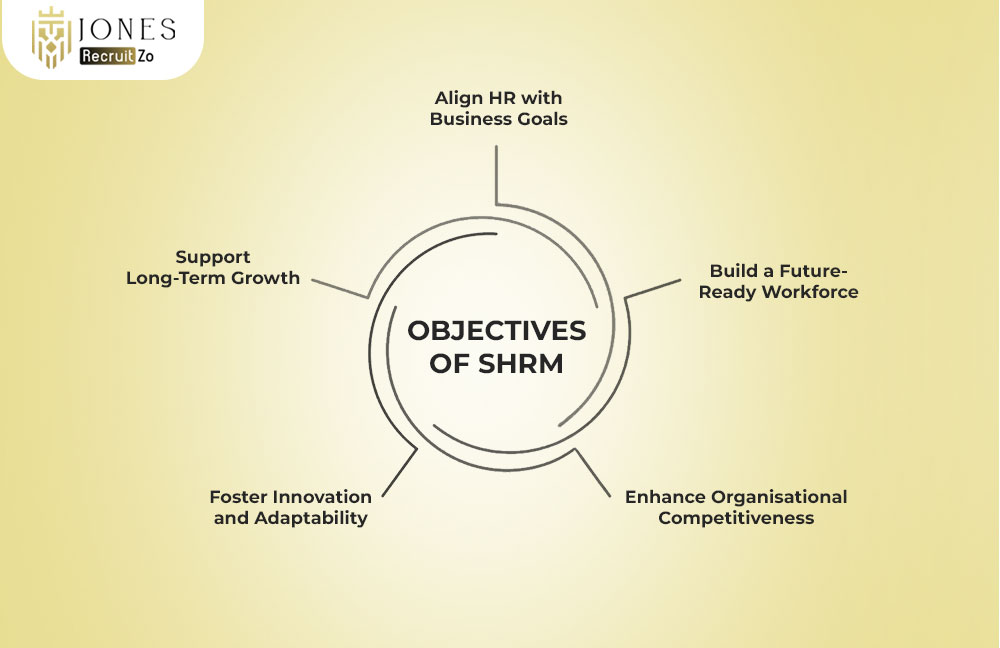
The objectives of SHRM go beyond daily management, focusing on long-term growth and strategy. Here’s how SHRM functions:
Align HR with Business Goals
Strategic Human Resource Management (SHRM) guarantees that workforce planning and HR activities align with an organisation’s goals and objectives. It brings together human capital management and organisational strategy. Such alignment enables HR to facilitate business growth instead of merely providing support.
Build a Future-Ready Workforce
Anticipating the skills and workforce of tomorrow, SHRM equips employees for the organisational needs for the long term. It places strong emphasis on upskilling, reskilling, and talent development. This approach positions the organisation to pivot as the industry evolves.
Enhance Organisational Competitiveness
SHRM enhances competitiveness by making certain the company attracts and retains the best talent. It enforces policies that encourage innovation, efficiency, and teamwork. Effective SHRM practices offer a company a competitive edge.
Foster Innovation and Adaptability
SHRM practices encourage innovation-focused approaches, as today’s environments are fast-paced. It offers employees policies that empower them to take risks, learn, and change at a fast pace. Such organisational changes improve an organisation’s chances of surviving external threats.
Support Long-Term Growth
SHRM is designed to support sustainability and long-term expansion. It ensures HR initiatives are not only effective today but also beneficial for future needs. This positions the organisation for steady growth and market leadership.
Key Differences Between HRM and SHRM
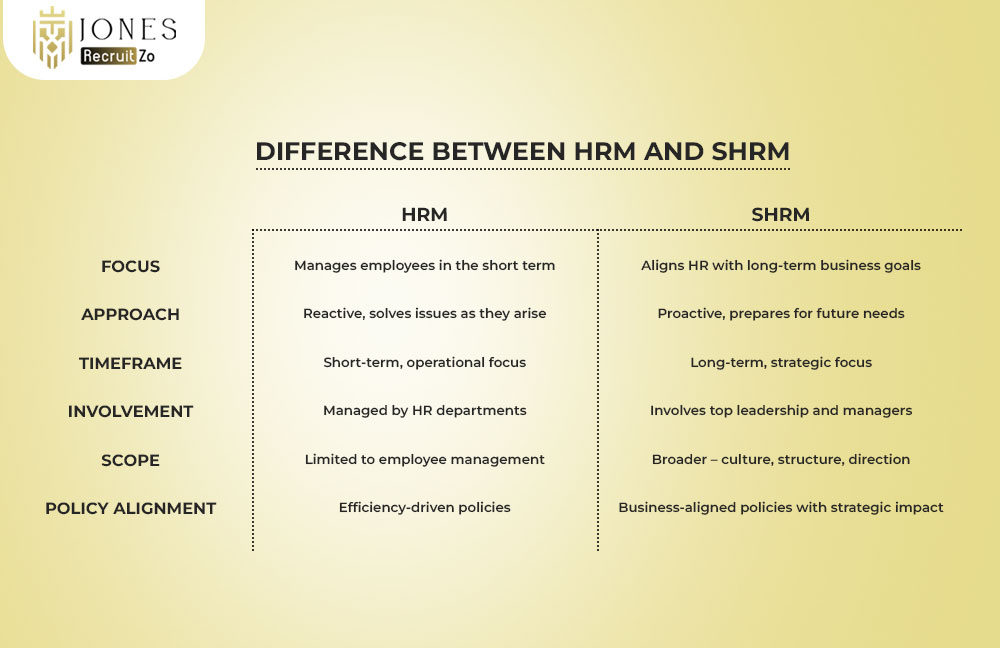
While HRM and SHRM are interconnected, their scope and approach vary significantly. Below are the major differences:
Focus
In HRM, the main focus is on managing employees in the short term, while SHRM focuses on integrating human resource policies into the overall strategic plan of an organisation. This is so that HRM can sustain the current productivity of the workforce, while SHRM can plan for where the business aims to be.
Approach
HRM has a reactive approach to managing the workforce, dealing with issues when they come up. SHRM is a proactive method which seeks to cater to the future needs of the organisation. This makes SHRM far more strategic in preparing for challenges as well as opportunities.
Timeframe
HRM operates within an operational time frame, while SHRM extends its focus to the long-term, strategic goals of an organisation. Organisations that effectively integrate both have the ability to sustain operations today and plan for the future.
Involvement
While HRM is handled by HR departments, SHRM requires the participation of top executives as well as senior managers. This ensures that the oversight of HR matters integrates concern for employees with the fulfilment of the business’s strategic plans.
Scope
The scope of HRM is restricted to managing employees. Within the broader context of organisational development, SHRM helps shape the company’s culture, structure, and overall direction, as well as provides oversight to HR functions.
Policy Alignment
HRM policies are designed for efficiency, while SHRM policies are aligned with business goals to ensure strategic impact. This alignment ensures HR becomes a value-adding partner rather than just an administrative function.
FAQs
1) What is the difference between HRM and SHRM?
If we consider their objectives, HRM is concerned with the handling of employees and operations on a day-to-day basis. On the other hand, SHRM is concerned with ensuring that HR practices are in line with the organisation’s goals on a long-term basis. The difference is SHRM is concerned with the implementation of the organisation’s strategies alongside HRM.
2) What is HRM (Human Resource Management)?
As an abbreviation of Human Resource Management, HRM is in charge of handling all the functions that deal with an organisation’s workforce, such as recruitment, training, payroll, and statutory compliance. It also aims to aid the organisation in the achievement of its short-term objectives.
3) What is SHRM (Strategic Human Resource Management)?
SHRM deals with the strategic integration of human capital policies with the company’s objectives in order to guarantee sustained competitiveness. It makes the company more adaptable and ready for the future challenges in the business world.
4) How does HRM differ from SHRM in focus?
Whereas SHRM aims at the strategic integration of business and HR functions, HRM deals with the management of employees and operations. This illustrates that SHRM adopts a more comprehensive and future-focused methodology towards human resource management.