Key Insights
Differences Between HRM and HRD
HRM manages people, policies, and workplace processes to ensure smooth organisational operations. HRD, on the other hand, develops employees’ skills and potential to prepare them for future roles and responsibilities.
Human Resource Management meaning
HRM focuses on effectively managing workforce operations such as recruitment, payroll, employee relations, and compliance. It ensures stability and efficiency in the day-to-day functioning of the organisation.
Human Resource Development meaning
HRD emphasises building employee knowledge, capabilities, and leadership potential through structured training and development initiatives. It creates a future-ready workforce aligned with organisational growth.
Key functions of HRM and HRD
HRM handles employee management processes like hiring, compensation, and policy-making, ensuring smooth workplace operations. HRD, in contrast, focuses on long-term professional growth through career development, leadership training, and talent management.
What is Human Resource Management (HRM)?
Human resource management represents a strategic approach used to manage people in an organisation with specific policies and processes ensuring the smooth operation of the workforce. HRM usually comprises recruitment, employee welfare, remuneration, law, and measures put before performance. By managing employees according to organisational goals, HRM plays a critical role in the efficiency of the whole business.
Key functions of HRM
HRM functions are interconnected, each contributing to the effective management and growth of the workforce.
Recruitment and Selection
The attraction and hiring of candidates who meet the qualifications based on company needs and values.
Employee Relations
Maintaining positive relations among employees and between employees and management so that their cooperation may be fostered and disputes resolved.
Compensation and Benefits
Setting salary levels and incentive schemes, bonuses, and benefits so as to keep employees motivated and attractive to competitors in the job market.
Performance Management
The continuous improvement of employee performance through appraisals, feedback systems, and goal setting.
Policy Formulation
Creating a set of clear guidelines and policies that govern behaviour in the workplace so that justice and legal compliance are observed.
What is Human Resource Development (HRD)?
HRD develops skills, knowledge, and capabilities of employees. While HRM focuses on processes, HRD develops people to meet current and future organisational needs. Training is continuous in the HRD system to ensure that employees remain competitive through career development and leadership development in changing environments.
Key functions of HRD
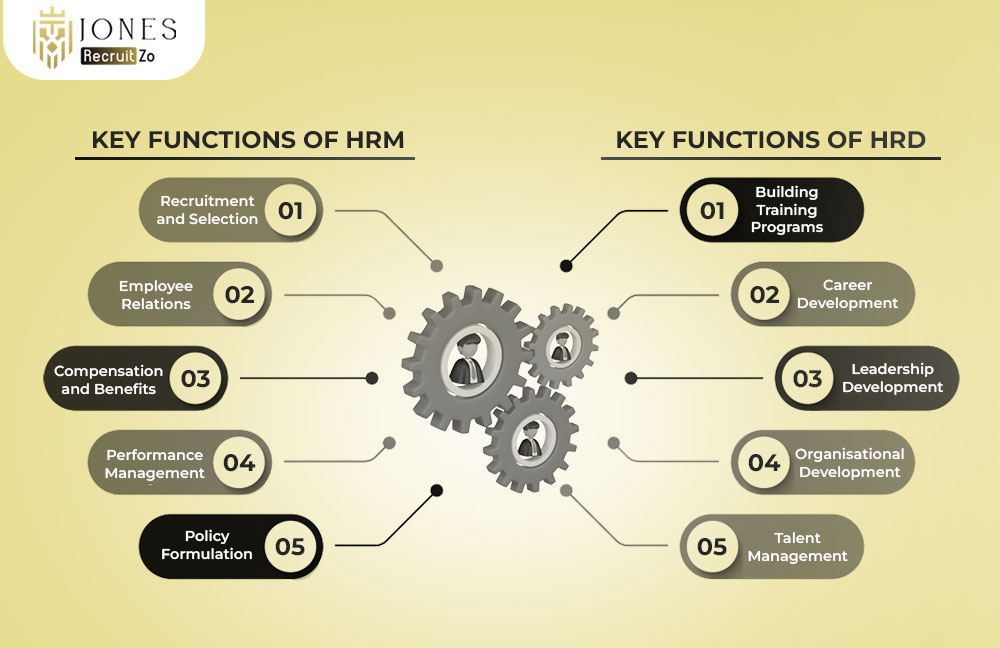
These functions aim to build a skilled, motivated, and future-ready workforce.
Building Training Programmes
Training programmes equip employees with new skills and update existing ones. They can be technical, behavioural, or role-specific, ensuring employees are job-ready and competitive. Ongoing training supports adaptability in a changing business environment.
Career Development
Career development initiatives help employees set and achieve long-term professional goals. This may involve mentoring, coaching, and internal mobility opportunities. When employees see growth prospects, they are more motivated to contribute to organisational success.
Leadership Development
Leadership development identifies high-potential employees and prepares them for managerial roles. This involves training in decision-making, communication, and team management. Strong leadership pipelines secure the company’s future stability.
Organisational Development
Organisational development focuses on improving systems, processes, and workplace culture. It aligns employee skills and behaviour with business objectives. The result is greater efficiency, innovation, and adaptability.
Talent Management
Talent management ensures the organisation attracts, develops, and retains top performers. It includes succession planning, skill mapping, and performance tracking. This helps maintain a strong workforce and reduces reliance on external hiring.
Key Differences Between HRM and HRD
While HRM and HRD are closely related, they have distinct roles in managing and developing employees. Below are the main differences:
Definition
HRM is concerned with the management of employees to ensure smooth and efficient operations. HRD is concerned with developing the employees, enhancing their skills, and promoting their growth.
Primary Focus
HRM mainly focuses on workforce administration; however, HRD focuses on continuous learning and development.
Scope
HRM has a wider scope that concerns recruitment, compliance, and employee management. HRD has a narrower scope in that its concern is skill-building and professional growth.
Timeframe
HRM, being more immediate, is concerned with short-term needs of companies, such as filling up positions and so on, while HRD is concerned with long-term objectives, preparing employees for future challenges.
Tasks
Payroll, internal recruitment, and workplace discipline constitute some of HRM’s tasks. Training programmes, succession planning, and capability development are activities considered under HRD.
Goal
The goal of HRM is to make operations efficient. The aim of human resource development is to either produce a skilled workforce, or create an adaptable workforce or whichever it is, to develop an adaptable and future-ready workforce.
Approach
HRM looks at meeting demand for a workforce reactively, while HRD looks at preparing employees for future opportunities and challenges proactively.
Benefits of Balancing HRM and HRD

An organisation that effectively balances HRM and HRD gains both operational stability and a highly capable workforce.
Higher Employee Retention Rates
An employee tends to stay with an organisation that shows good management and development interest in him or her. Thus, attrition reduces, and more loyalty gets built into the workforce.
Boosted Workplace Productivity
HRM functions and HRD interventions together have a positive influence on employees’ productive behaviours. Competent employees supported with effective systems ensure better productivity.
Strong and Positive Organisational Culture
HRM sees that policies are fair, while HRD keeps the employee engaged through learning opportunities. Along with these, the organisation promotes an environment of trust, friendship, and commitment.
Enhanced Talent Pipeline for Future Roles
When HRM and HRD are balanced, the business keeps a consistent flow of skilled people ready for lead and critical positions, cutting down dependency on external recruiting and leading to eventual business continuity.
Increased Organisational Agility
When a continuously managed and developed workforce meets change, it responds faster than the untrained and unmanaged one, putting extra resilience into the organisation against challenges and market changes.
FAQs
1) What is Human Resource Management (HRM)?
HRM is the management of employees and workplace operations to satisfy compliance, fairness, and productivity-related matters.
2) What is Human Resource Development (HRD)?
HRD is about improving the skill sets, knowledge, and capabilities of employees through systematic programmes including training and career development.
3) What is the difference between HRM and HRD?
HRM looks at present workforce processes; HRD looks at developing employees for jobs of the future through ongoing learning.
4) What are the key functions of Human resource management?
They include recruitment and selection, employee relations, compensation, performance management, and policy formulation.
5) What are the key functions of human resource development?
They include training, career development, leadership development, organisational development, and talent management.














