What is a Contingent Worker?
A contingent worker refers to an individual hired on a non-permanent basis by a company. Examples include project workers, those hired for seasonal work, or workers with short-term contracts. Unlike permanent workers, contingent workers are not provided long-term job security, benefits from the organization, or accounting within an organizational payroll structure.
Instead, they exist independently or through staffing agencies. Often they are experts in their particular fields and come in to support businesses for certain needs without undergoing long-term commitments as regular employment would.
Types of Contingent Workers
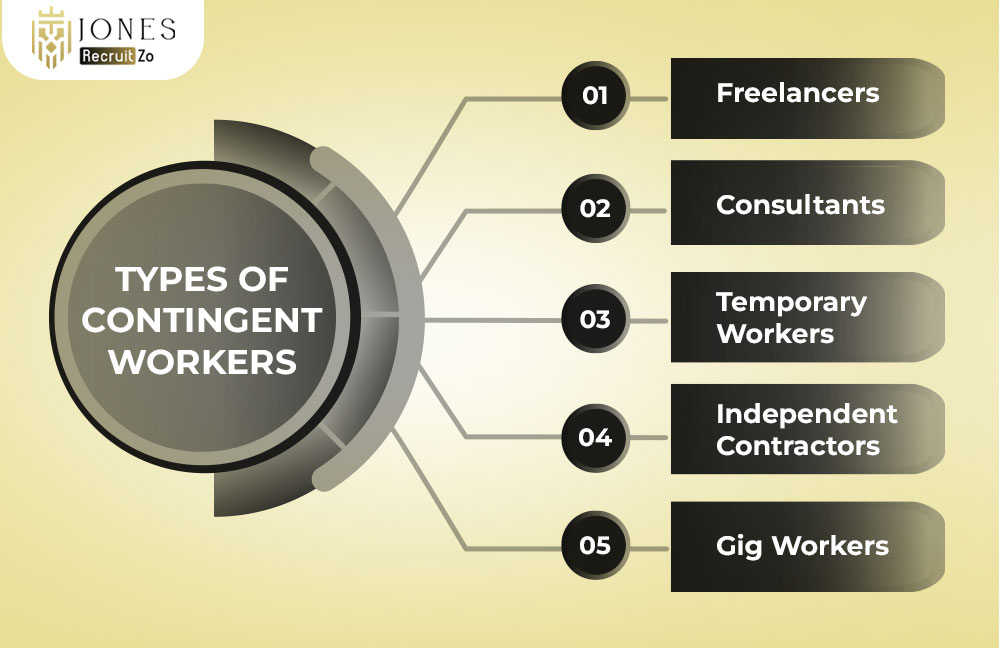
The contingent workforce encompasses a diverse group of professionals with different working arrangements. Below are the main types:
Freelancers
Freelancers are often considered self-employed individuals who deal with various clients on a project basis. Usually, these include creatives — graphic designers, content writers, marketers, and web developers, for instance. Freelancers set their own working hours and are responsible for paying their own taxes and benefits.
Consultants
Such specialists are brought to bear on a problem so their advice may be considered next to theirs. In most cases, they can be independent agents or, depending on their firm, be dependent. Working with objectives is usually determined whether it’s for improvement of operational efficiency, marketing strategy, or compliance process
Temporary Workers
Temporary workers, known simply as “temps”, are employed for numbered days, and one of their objectives is to fill in for training gaps. They are brought in through temporary staffing companies, acting as surrogates for full-time employees who are on vacation or on sick leave or during times of heavy workload. The contracts can last anywhere from a few days to many months.
Independent Contractors
Independent contractors provide services in a business-to-business model. They control how the work is performed and usually work for specific deliverables. One may mostly come across contractors in IT, construction, and consultancy.
Gig Workers
Gig workers get picked for jobs at the instance of an employer: work on whatever must be done, anytime and anywhere. Platforms such as Uber, Swiggy, and Upwork have transformed the gig economy into a vast opportunity where workers can flexibly take on brief tasks like deliveries, rides, or micro-jobs, usually for an hour or two.
Differences Between Contingent Workers and Employees
Although contingent workers and employees may perform similar roles, there are fundamental differences between the two.
Employees are typically hired on a full-time or part-time basis with long-term intentions. They receive a fixed salary, are entitled to benefits like healthcare and paid leave, and are covered by employment laws and regulations.
Contingent workers, on the other hand, are not integrated into the organizational structure in the same way. They do not receive employee benefits and are responsible for managing their own taxes. They usually work with more autonomy and have limited job security but also enjoy greater flexibility.
Why Companies Hire Contingent Workers?
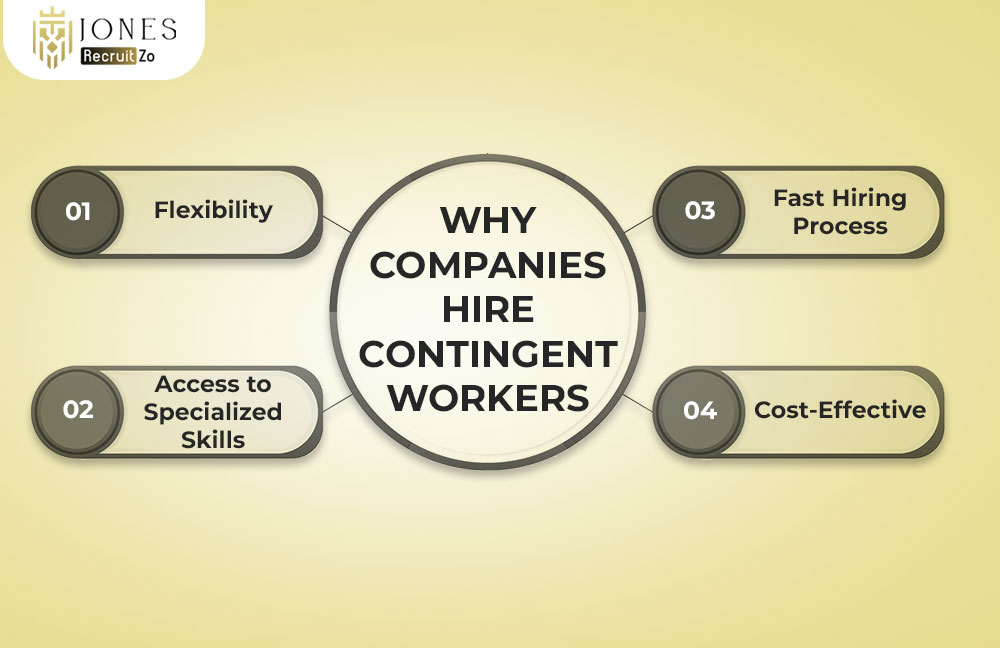
Businesses are increasingly relying on contingent labor for several strategic reasons. Here’s why this model is so appealing:
Flexibility
Contingent workers allow companies to scale their workforce up or down based on workload and project requirements. Such flexibility comes into play with a lot of roles during the peak season or in the early stage of launching a new initiative.
Access to Specialized Skills
The need to engage contingent workers is whenever higher skills demanded in the industry can be supplied by the workers, more so for a short duration or for a highly niche-related project.
Fast Hiring Process
Since contingent roles do not normally engage time-consuming screening and onboarding procedures typical for permanent hires, organizations fill these positions in record time – the shortest being a matter of days.
Cost-Effective
Since contingent staff may become the only advantage when companies pay for retirement, medical plans, or office space, overhead is very cheap – set into the price of worker retention.
How to Manage a Contingent Workforce?
Effectively managing a contingent workforce requires different strategies than managing traditional employees. Here’s how organizations can ensure smooth operations:
-
Use a Vendor Management System (VMS)
A VMS will help the organization in sourcing, onboarding, and managing contingent workers in an efficient manner. It centralizes contracts, tracks hours, and collects data on vendor performance.
-
Create Clear Policies and Guidelines
Even though contingent workers are not full-time employees, a set of rules for communication, data access, deadlines, and confidentiality must be in place so as not to create confusion and ensure accountability.
-
Develop Strong Communication Channels
Clear and open communication channels should be created and maintained. Contingent workers must know what to expect of themselves and should be able to reach out to the stakeholders and project leads for assistance, if need be. Tools such as Slack or Microsoft Teams are very convenient for collaborative purposes.
-
Streamline Onboarding Processes
Fast and smooth onboarding gets contingent workers off to a good start. Grants access to all the tools, documentation, and contacts they need without delays.
-
Track Performance and Output
Use KPIs or regular check-ins to assess the progress and quality of work performed by contingent workers. Constructive feedback helps keep up performance and ensure that expectations are met.
-
Plan for Offboarding
To the extent a project is completed, offboarding should be made smooth, just like onboarding. Getting feedback, closing system access, and ensuring all documentation or project work is completed and handed over.
FAQs
1) What is a contingent worker?
A contingent worker refers to a professional hired temporarily for a specific job, project, or timeframe and is not considered a permanent employee by the organization.
2) What are the different types of contingent workers?
Typical types of contingent workers include freelancers, consultants, temps, independent contractors, and gig workers.
3) What are the Differences Between Contingent Workers and Employees?
In contrast to employees, contingent workers do not get company benefits, work largely short-term contracts, and remain off the company payroll.
4) How to Manage a Contingent Workforce?
A Vendor Management System-fied approach: create policies and communicate them; do streamlined onboarding/offboarding; track performance.














